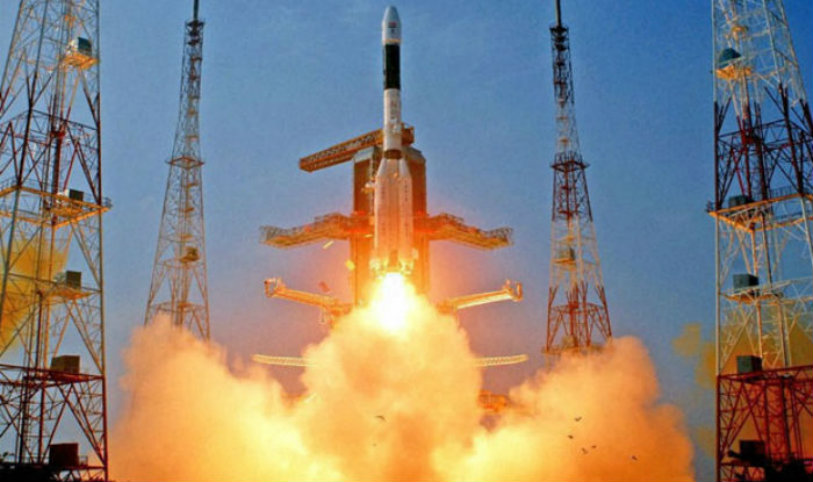
Yesterday is marked as yet another important day for India and its contribution to space and technology. On Monday, Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) launched GSLV Mark III rocket successfully. The communication satellite GSAT 19 was on board of the launch vehicle and was then separated.
At 5:28 P.M. at the Satish Dhawan Space Center in Sriharikota marked the successful lift off of the GSLV Mark III rocket. The mission was just 16 minutes long. The rocket has the capacity to carry 4 tons of payload, making it the best among all the Indian rockets. The successful launch has given way to launch heavier satellites in the future without having to rely on international space agencies.
The communication satellite launched with the rocket, GSAT 19 is the heaviest launched by India weighing 3126 kgs.
A.S. Kiran Kumar, chairman of ISRO was quoted saying, “It is a historic day, both the GSLV Mark III and the GSAT-19 launch have been successful. We are looking forward to its (GSAT 19) operations.”
Prime Minister Narendra Modi and President Pranab Mukherjee both took to Twitter to congratulate the ISRO team on the successful launch.
Congratulations to the dedicated scientists of ISRO for the successful launch of GSLV – MKIII D1/GSAT-19 mission.
— Narendra Modi (@narendramodi) 5 June 2017
Heartiest congratulations to ISRO on the historic launch of GSLV-Mk III #PresidentMukherjee
— President of India (@RashtrapatiBhvn) 5 June 2017
In the year 2001, ISRO launched its first GSLV satellite that had of 1,500 kgs of payload capacity. The ISRO developed the model and upgraded it to 1,900 kgs. Then nine years and five flights later, came the GSLV Mark II with 2,200 kgs payload capacity. The main challenge for GSLV Mark III was developing a homegrown cryogenics engine. A cryogenics engine uses gas that has been liquefied and then is boiled and turned to gas in the rocket, using the gas to power it.
But India managed to successfully complete and test an indigenous cryogenic engine in 2014. The first experimental flight of Mark III was done on 18th December 2014, which was a success. The three years were spent on conducted different tests for each stage of the rocket to ensure proper functioning. It has been estimated that the total project cost was Rs. 2,900 crores.