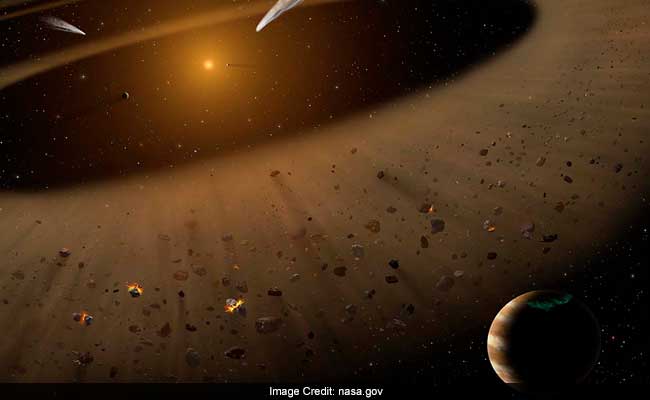
NASA scientists have found a planetary system that is similar to our solar system and is located 10.5 light years. The scientists said that this is very similar to our planetary system. The scientists also said that the location provides right access to research how planets are formed around the sun.
This solar system 2.0 is located in the southern hemisphere of the Eridanus constellation. According to researchers from the University of Arizona in the US, Epsilon Eridani is the closest star to the solar system that resembles the early sun.
The studies also say that the debris disk around Eps Eri was left over material after the construction of the planetary system. The debris can be of different forms like gas, dust, small rocks and also icy bodies. They can form broad spread belts or concentrated belts of debris. The debris belt surrounding Eps Eri is similar to the Kuiper Belt, which is a region at the edge of the solar system. This Kuiper belt has hundreds of thousands of icy rocky objects.
The scientists also said that the measurement of motion shows that the Eri is the similar size of Sun. It also has been proven that a similar to Jupiter planet revolves similar distance of Jupiter from Sun. In the Eri system, based on the new Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) images, researchers were able to distinguish between two theoretical models of the location of warm debris, such as dust and gas.
With the help of SOFIA, Kate Su of the University of Arizona along with her research team said that warm material was found near Eps Eri. It was similar to the first model that was determined before. The team said that this belt was a narrow belt and not a broad continuous disk. The team also found warm materials between 25-40 microns, which were not detectable by the ground based observatories. Kate Su, speaking about this said, “The high spatial resolution of SOFIA combined with the unique wavelength coverage and impressive dynamic range of the FORCAST camera allowed us to resolve the warm emission around Eps Eri, confirming the model that located the warm material near the Jovian planet’s orbit.”
The study was published in The Astronomical Journal. Su in the journal explained that a planetary mass object is needed to stop the sheet of dust from the outer zone, similar to Neptune’s role in our solar system. It really is impressive how Eps Eri, a much younger version of our solar system, is put together like ours.